Flux on the gums is an extremely unpleasant, but quite common phenomenon, which is an inflammatory process in the periosteum area. The word “flux” is of German origin and is translated as “flow, flow.” Today, this term is not commonly used in professional circles. Instead, experts use the scientific name of the disease - odontogenic periostitis. In most cases, it overtakes the most patient patients who diligently avoid visiting a professional dentist for a long time. As a result, due to laziness or fear of the dentist, the patient receives severe swelling of the gums, constant dull pain, and in some cases, high fever.
Despite the fact that the phenomenon in question cannot be called a rarity, this does not make it any less harmless. The advanced form of periostitis is quite dangerous, so the health of the oral cavity and teeth should be taken as seriously as possible, and at the first signs of inflammation you should consult a specialist as soon as possible.
Content:
- Why does it occur
- Signs
- How it proceeds
- Features of the development of periostitis in children and adults
- What happens if you don't undergo therapy?
- How to remove flux
- How to speed up recovery
- Preventive actions
An inflammatory dental disease that affects the periosteum tissue is called periostitis by dentists.
It is popularly known as flux. It is easy to recognize on your own - a painful abscess forms on the gum, which does not go away for a long time. It is unwise to fight this disease without medical help. When it appears, you should definitely make an appointment at a dental clinic and, during an in-person examination, find out from the doctor how to remove the flux without negative consequences for health.
It is simply impossible to ignore periostitis. It is usually accompanied by acute throbbing pain. Sometimes it can even lead to fever and a sharp decrease in performance. When there is a lot of pus in the “bag”, it bursts. Then the purulent masses flow out, and the symptoms cease to be so bright.
Diagnostics
Before proceeding with dental flux treatment, the doctor must conduct an appropriate diagnostic examination. The exact diagnosis is determined based on data obtained during a clinical examination and x-ray diagnosis. Laboratory tests allow you to accurately determine the stage of the inflammatory process. Only after making an accurate diagnosis will a specialist be able to decide what to do with gumboil and which method of treatment in this particular case will be optimal.
Why does it occur
In order to understand how to remove flux, it is necessary to establish what led to its appearance. If the provoking factor is not eliminated, the disease may return. Among the main reasons for the violation:
- untreated deep caries;
- a large amount of hard plaque extending far under the gum;
- dental root cyst;
- inflammatory lesion of the gingival pocket;
- receiving mechanical injuries;
- general hypothermia of the body (especially against the background of reduced immunity);
- poor oral hygiene.
According to statistics, most often the disease occurs precisely because of advanced caries and pulpitis. If there is a large “hole,” the infection easily penetrates deep into the dental tissues, affects the surrounding structures and causes nerve destruction. Then pulpitis develops.
If left untreated, it will become chronic. The pain will become mild, but this does not mean that the disease has gone away. It’s just that now it’s happening secretly. The infection will continue to destroy the internal structures of the diseased unit. As they die, narcotic masses will begin to be released. To remove them, an abscess forms on the gum. This is flux.
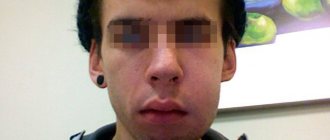
If it is localized on the periosteum of the upper jaw, then the upper lip and the area under the eye swell. If inflammation progresses in the lower jaw, the chin and cheek swell, and the lymph nodes become painful.
Do not heat the inflamed area
When people think about how to treat flux, they usually remember various traditional medicine, in particular compresses and heating (for example, with salt), rinsing with hot herbal decoctions. If you are going to treat flux in this way, then you are making a grave mistake. In 80% of clinical cases, the disease occurs in a purulent form, that is, purulent exudate accumulates in the inflamed periosteum, on which heat has a stimulating effect.
Warming the cheek is contraindicated
If you heat the diseased area, the blood supply to the inflamed tissues will be stronger, and the infection will spread to deeper layers, which will provoke even greater swelling, pain and intoxication of the body. If, under the influence of heat, pus enters the blood or lymph, it can spread to adjacent organs, cause damage to the heart, brain, liver and kidneys, and lead to sepsis (blood poisoning).
It is not forbidden to rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions (chamomile, sage), as they help relieve acute inflammatory processes and reduce pain and swelling. But in this case, the liquid should be slightly warm or at room temperature.
Signs
You can understand that periostitis has developed by the following symptoms:
- tooth pain;
- swelling of the gums;
- an abscess at the base of the diseased unit;
- increased pain when pressing on the affected area;
- swelling of the cheek;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the lymph nodes.
If these symptoms occur, you should make an appointment with the dentist as soon as possible. In the early stages, the problem can be eliminated quite easily and quickly. Delay is fraught with health-threatening complications.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as additional ones. They allow you to quickly cope with the infection and stop the inflammatory process. The following methods can achieve good results:
- Fluctuarization. The inflamed tissues are exposed to low voltage current.
- Electrophoresis with lidase. Electrical current is applied to the tissue, allowing the drug to be effectively distributed.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. The method is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field.
- Ultrasound therapy. The effect of ultrasound on infected tissues accelerates their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Damaged tooth tissue is treated with a laser beam.
How it proceeds
The disease progresses through several successive stages:
- Acute serous. Spreads quickly. In just two or three days, a large, painful “bump” forms, with pus inside. The cheek tissues swell.
- Acute purulent. The pain becomes more pronounced, the person feels an unpleasant pulsation. The mucous membrane in the area of the affected unit turns red and swells. Body temperature rises.
- Acute diffuse. The swelling becomes voluminous. It can go under the eye or onto the nose. The patient's appearance changes significantly for the worse.
- Chronic. The painful process fades away and is replaced by a chronic one. The patient may mistakenly think that the problem has disappeared without a trace. In fact, it only calmed down for a while. Periodically, the disease will recur.
The sooner a sick person consults a doctor, the higher his chances of a speedy recovery.
Self-prescribed antibiotics are a path to the chronic stage or complications
Treating gumboil at home with self-prescribed antibiotics is not a good idea for the following reasons:
- each medicine affects different types of microorganisms1, and a person who is not related to medicine is unlikely to be able to understand which bacterium is causing the inflammatory process in him,
- thinking about how to treat flux at home and deciding to take antibiotics, you quickly transfer the disease to the chronic stage. For a while, all the vivid symptoms really disappear, you experience relief, since the medications suppressed the growth of bacteria, but did not completely destroy them (after all, you did not cure a bad tooth!). The danger is that microorganisms can reactivate at any time, and they will become resistant to the type of antibiotics that you took. This means that you will have to fight the disease for a very long time, and you will undermine your immunity.
Do not self-prescribe antibiotics
Features of the development of periostitis in children and adults
In adults, the disease usually has vivid symptoms. Most often it is caused by bad habits and ignoring the rules of oral hygiene. The tissues surrounding the root become inflamed. Persistent pain forces a person to seek dental care.
In children, flux usually progresses with mild symptoms. This is due to the fact that in children the immune system reacts less actively to abnormal processes in the oral cavity. Even if the purulent “bump” does not hurt the child, a consultation with a dentist is still required.
General treatment
Methods depend on the reasons that caused the flux. The only exception is periostitis, which develops against the background of periodontitis. In this case, immediately after opening the abscess, the doctor begins periodontal treatment. No medical manipulations with the tooth are required. In other cases of dental disease you need to treat:
- Pulpitis. First, the dentist drills out carious cavities and performs pulp removal. After this, endodontic canal treatment is performed.
- Periodontitis. Treatment depends on whether depulpation and canal filling have been previously performed. If periodontitis has developed for the first time, the doctor will remove the pulp, clean and fill the canals. If filling of the canals has already been performed previously, they need to be unfilled and treated again. Since it is very important that the pus comes out of the flux completely, when treating complicated pulpitis and periodontitis, a temporary filling is not placed.
- Tooth after restoration. At the first stage, the doctor is faced with the task of completely removing inflammation. After this, the damaged tissue of the root apex is removed. If the condition of the root allows, the tooth is restored again using a core tab or pin and an artificial crown. When the damage is very severe, it is more advisable to remove the tooth.
What happens if you don't undergo therapy?
It is unacceptable to treat purulent gum lesions as a minor dental disorder. It is very insidious and rarely disappears without a trace on its own. Often, if treatment is refused, the following occurs:
- Abscess. It is a consequence of a long-term presence of a pus-filled sac in the area of the tooth root. The abscess grows and then ruptures.
- Phlegmon. Represents an extended lesion. It usually occurs after a rupture of a purulent sac, if the patient does not comply with the dentist’s instructions, does not rinse the mouth with a special antiseptic solution, or apply anti-inflammatory gels.
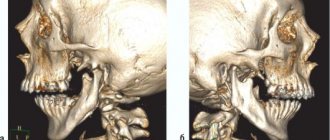
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw. It occurs if the gums are not treated for a very long time. The pathological process spreads to the jaw bone, which is very dangerous.
- Inflammation of individual sinuses of the skull. It is also diagnosed with advanced periostitis. The maxillary, frontal and sphenoid sinuses are affected.
It is extremely rare that the disease affects brain tissue. Then the person may even die.
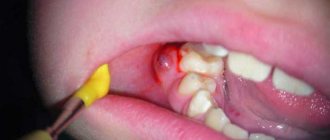
Opening an abscess on the gum
The abscess is always opened. This reduces the risk of spontaneous opening, which can cause complications. The flux is opened under local anesthesia. If the patient has panic or other indications, the doctor may choose a different method of anesthesia.
A small incision is made on the anesthetized gum in the area of the gumboil, no more than 2 cm in length. After the dissection, the doctor completely cleans and sterilizes the purulent cavity and treats it with antiseptics. A crust should not be allowed to form in the area of the incision, as it will interfere with the outflow of ichor and purulent contents. To do this, a drainage is inserted into the incision. After the cavity is cleared of pus, you can begin general treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate the causes that caused periostitis.
How to remove flux
To avoid purulent damage to the pulp zone and periosteum, you need to receive qualified dental care in a timely manner. In the early stages of the disease, in order to prevent further progression of the inflammatory process, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. It is mandatory to open the abscess. The wound is then cleaned and washed with an antiseptic.
In some cases, to prevent re-accumulation of pus, drainage is installed for several days. All surgical procedures are always performed under general anesthesia so that the patient does not experience pain.
To support the patient’s body, he is additionally prescribed a vitamin and mineral complex. If necessary, physiotherapy is included in the treatment course. Good results can be obtained using UHF and electrophoresis.
It is important to strictly follow all medical recommendations and under no circumstances interrupt antibiotic therapy. Treatment is considered successfully completed if pus is no longer released, pain does not occur, and the entire wound has healed. In some cases, after healing, a small bluish scar remains on the gum. You shouldn't worry about it. This means that the defeat was very deep. Over time, the gums will return to their normal appearance.
Alcohol after tooth extraction
Drinking alcohol-containing drinks after tooth extraction is strictly prohibited. A strict ban on alcohol in any quantity is valid for at least 3 days after surgery. If antibacterial therapy was prescribed, then for the entire period of treatment and healing. There are very important reasons for such a strict measure:
- alcohol first constricts and then dilates blood vessels, which leads to a surge in pressure and bleeding;
- strong drinks catastrophically reduce the body’s immune defense, which is very necessary to prevent complications after surgery;
- alcohol relaxes and relieves pain, so a person may not notice postoperative problems and trigger pathology;
- any medications (analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, antihistamines), often prescribed after tooth extraction, are not compatible with alcohol.
The ban applies to all alcoholic drinks - vodka, beer, wine, champagne, cider. Vodka can immediately cause severe bleeding, and in combination with a pharmaceutical drug - anaphylactic shock. Beer contains yeast, which gets into the wound hole and ferments, causing inflammation. Wine greatly reduces the body's defenses against external influences, which leads to wound infection and prolonged healing. Champagne and cider, among other things, are saturated with oxygen, the bubbles of which loosen injured tissue. Any other alcohol acts similarly and certainly does not contribute to recovery.
It is important to understand that even a small amount of alcohol can cause an unexpected reaction and serious complications after tooth extraction. Therefore, you should not take risks, but rather take care of yourself.
How to speed up recovery
To make healing go faster, it is important not only to follow the dentist’s instructions, but also to remember the rules:
- do not heat the area where the pus was located;
- do not take antibiotics or any other medications unless prescribed by a doctor;
- do not use any folk recipes without consulting your doctor;
- Until the wound is completely healed, do not use aspirin or any medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid.
If the “bump” appears again, it is recommended to immediately contact a dental clinic.
Anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics
The use of antibiotics helps relieve pain and stop acute inflammation. You can use antibiotics such as Trichopolum, Lincomycin, Ciprofloxacin, Flemoxin, Biseptol, Amoxiclav, Tsiprolet. Antibacterial drugs should not be used for more than five days to avoid microbial resistance in the body.
To reduce swelling and redness, you can additionally take Diazolin, Nimesil or Diclofenac, which have a local anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect.
Preventive actions
To reduce the likelihood of periostitis, you need to take care of your teeth and visit the dentist at least once a year. You can't start caries. As soon as a dark spot appears on the surface of the dental crown, it needs to be treated.
After eating, it is advisable to rinse your mouth with warm water. To make hygiene as high as possible, it makes sense to use not only a brush and toothpaste, but also dental floss and irrigators. It is very important to remove tartar every year at the dentist's office.
An important place in the issue of prevention is given to diet. You should eat as much fresh fruits, vegetables, and plant foods as possible. They require more thorough chewing and thus have a positive effect on the ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth. They also provide natural cleansing of crowns from soft plaque.
If you have any questions about how to remove flux, please contact the doctors at the Line of Smile dental clinic for help. We specialize in the treatment of this disease and know how to quickly rid our patients of it.
When and what can you eat after tooth extraction?
All dentists recommend that patients refrain from eating for several hours after tooth extraction. Depending on the complexity of the operation, the recommended time ranges from 2 to 6 hours. If everything went easily, the blood stopped quickly, then you can eat after 2-3 hours. A complex and painful operation requires complete rest for the oral cavity for 5-6 hours.
As for the menu itself, it should not be dense - a small snack is enough to start. The first meal should not contain hard, spicy, sour or hot foods. Various purees (potato, vegetable), soft porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat), mousse, yoghurt are suitable. Approximately this diet should be observed for 2-3 days.
On the 3-4th day after the operation, subject to good healing, the diet can be diversified with pasta, cereals, boiled meat and fish. But you still can’t eat hard foods, such as crackers, apples, nuts. You should avoid smoked and salty foods (sausage, canned food, deli meats) until the gums have completely healed. Throughout the recovery period, it is important to monitor the temperature of the food - nothing too hot or very cold.
Parents of children, and adults themselves, often wonder if ice cream is okay. Yes, it can be eaten a few hours after removal. Cold constricts blood vessels and helps stop bleeding, and also relieves inflammation and swelling. In addition, ice cream serves as a good sedative for a child who has experienced stress during surgery. The main thing is not to overdo it and not get a cold in your throat - infections in the respiratory tract are absolutely unnecessary during this period.