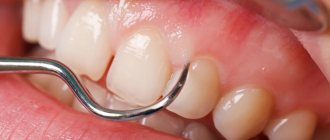
Periodontitis is a disease of the oral cavity in which the periodontal tissues are damaged, the jaw bones are destroyed, and teeth become loose and fall out. Due to the presence of chronic infection in the so-called periodontal pockets, the entire body suffers. Signs of periodontitis include bleeding gums, bad breath, pain and discomfort in the gums.
The disease occurs as a result of insufficient oral hygiene, defects in fillings and prosthetics and other reasons. Thus, poorly installed fillings and restorations, teeth molded together, stamped crowns, and improper manufacturing of metal-ceramics lead to periodontitis in almost 100% of cases. The level of service at Family Dentistry eliminates the possibility of such medical errors, which can cause disease.
The prevalence of periodontitis is high. According to available data, only 3% are completely healthy people. The rest of the population needs professional help to varying degrees. The disease can only be overcome with an integrated approach to treatment, which is practiced at Family Dentistry. We involve various specialists in the consultation, diagnosis and treatment of patients, with the help of whom a joint treatment plan is developed.
Treatment of periodontitis at Family Dentistry is carried out using surgical and non-surgical methods. Non-surgical methods include preventive cleaning of the tooth surface, supportive periodontal therapy, hygiene measures and other methods. Surgical methods are used to treat severe periodontitis. Family Dental specialists will select an individual hygiene program that will help you prevent the development of periodontitis. Come for a consultation with a periodontist and start treatment on time. At Family Dentistry, periodontist surgeon T.R. will help you. Zhazykoev
What is periodontology and periodontology?
The tissues that are located around the subgingival part of the teeth are called periodontium. It has a multilayer structure: gums (mucous membrane covering the teeth in the cervical area); dental root cement; periodontium (tissue between the cementum and the socket); periosteum (tissue covering the bone) and alveolar process (part of the jaw tissue on which the dental units are located). These tissues securely hold the tooth in the socket (alveolus). The branch of dentistry that studies the periodontium, its functions and diseases is called periodontology.
Causes and symptoms of periodontal problems
How do you know if your periodontist needs help?
Even a non-specialist can easily notice symptoms indicating the onset and progression of a pathological process. First of all, this is redness of the gum tissue around one, several or all teeth. There may be bleeding and/or itching of the gums, increased sensitivity when eating or brushing, and varying degrees of swelling. Often inflammation is accompanied by the appearance of bad breath. When the pathological process is far advanced, pus forms and the gum line drops significantly, exposing the necks of the teeth. Symptoms depend on how deeply the tissue is affected. Diseases to which periodontal tissues are susceptible:
- gingivitis - the name of the disease itself is translated as “inflammation of the gums.” The most common form is catarrhal form, manifested by bleeding and excessive sensitivity of the gum tissue. There is also a hypertrophic variant of the disease, characterized by an increase in the density of the gums and their growth. The ulcerative form is manifested by ulcerations of the gingival surface, turning it gray and even the death of some areas.
- Periodontitis is most often a consequence of untreated gingivitis. It is expressed by the formation of purulent contents, atrophy of the alveolar process, and exposure of the neck of the teeth. As a result, teeth become loose, periodontal pockets increase (up to 5 mm), and pain appears. The most serious complications are tooth loss, bone tissue destruction;
- periodontal disease. Dentists have different views regarding the classification of this disease. Some believe that this is an aggressive form of periodontitis, while others classify it as a separate category. But, nevertheless, the protocol for its treatment does not change depending on the type of classification. With this disease there is no purulent discharge or formation of periodontal pockets.
Causes of periodontal inflammation:
- poor oral hygiene;
- mechanical, chemical, thermal injuries of the gums;
- pathology of occlusion (bite);
- improper dental prosthetics, resulting in injury to the gum tissue;
- excessive smoking;
- weakening of the immune system due to various diseases, stress, hormonal changes in the body;
- diabetes mellitus, HIV, oncology;
- hereditary factor.
When is it time to contact a periodontist?
The most common periodontal diseases are gingivitis and periodontitis.
Periodontal disease is much less common. The treatment of these diseases is carried out by a periodontist. But most often an integrated approach is required. If necessary, in our clinic you can visit a dentist, surgeon, orthopedist and orthodontist. This will not only relieve the unpleasant symptoms of gingivitis or periodontitis, but also eliminate the cause of their development. Many patients ignore the first symptoms of this pathology, considering them to be of little significance. Meanwhile, an inflammatory process that has just begun is much easier to stop than an advanced one. Treatment in this case will not require surgery and will be much cheaper. It is necessary to contact a periodontist if you have the following symptom complex:
- Bad breath;
- Bleeding, swelling, sore gums;
- Food getting stuck between teeth;
- Accumulation of plaque and tartar.
At the stage when the patient is concerned about such problems, they can be eliminated in literally 1-2 visits. That is why the doctors of the Dental Studio
It is not recommended to delay a visit to a specialist.
Delayed treatment can lead to the following negative consequences:
- Formation of deep periodontal pockets;
- Tooth mobility;
- Recession (lowering) of gum tissue;
- Premature tooth loss;
- Pain when eating.
Conservative periodontology
is a branch of dentistry that uses non-surgical methods for diagnosing and treating periodontal diseases. They are preferred for the vast majority of patients, as they are non-invasive. Conservative, that is, non-surgical methods are used whenever surgery can still be avoided. Only when they are ineffective do they move on to more radical measures.
Treatment of gums in periodontology begins with a consultation with a specialized specialist. Appointment at the Dental Studio
led by doctors with many years of experience. The doctor will conduct an examination and, if necessary, send the patient for an x-ray to assess the condition of the bone tissue. As part of the treatment and prevention of periodontal diseases, Vector therapy is carried out. Using the Vector device, supragingival and subgingival deposits, which are the cause of microbial inflammation, are removed.
In modern periodontics, laser gum treatment is becoming increasingly popular. This technique is in great demand and enjoys well-deserved trust. In our clinic, the doctor uses the Optodan laser device. Low-impulse laser light of the infrared spectrum promotes the regeneration of affected tissues, restores normal microcirculation, and suppresses the activity of pathogenic microflora. The procedure is considered physiotherapeutic, is well tolerated by patients, is painless, and shows good results during a course of treatment. The duration of the course and the intervals between procedures are determined individually, taking into account the degree of development of the pathological process and the characteristics of its course in a particular patient.
Prices for gum treatment in periodontics are available to a wide range of patients. It is important to correctly assess the significance of treatment: an advanced process inevitably leads to loosening and loss of teeth. Prosthetics and implantation will cost much more.
Methods for treating gum inflammation
Treatment of gum inflammation is a complex of therapeutic and (or) surgical measures aimed at eliminating the causes of inflammation and restoring periodontal functions.
Treatment is prescribed by a periodontist after a visual and hardware (if necessary) examination. The list of therapeutic measures depends on the factors that initiated the onset of the disease and the severity of the pathological process. Treatment methods for periodontal diseases:
- elimination of the causes that caused the pathology (for example, bite correction, replacement of dentures, stabilization of blood glucose levels, etc.);
- professional cleaning with an ultrasonic scaler and AirFlow device;
- applications and rinsing with antiseptic and medicinal preparations;
- administration of drugs by injection into the gingival surface;
- massage to strengthen gums;
- electrophoresis and other physiotherapy procedures;
- excision of gingival margins (for hypertrophied gingivitis);
- course of antibiotics and vitamins;
- treatment with the “Vector” device;
- laser treatment of periodontal pockets, in severe cases – curettage (surgical cleansing);
- splinting loose teeth;
- plastic surgery of gum recession;
- bone grafting.
Important: periodontists of the “Smile” network of clinics are proficient in modern methods of treating periodontal tissues; our centers are equipped with the latest equipment for diagnosing and treating gum inflammation. You can make an appointment for a consultation by phone or by using the “Book online” or “Request a call” options on our website.
Modern approaches to conservative treatment of periodontal diseases (review)
Bibliographic description:
Modern approaches to the conservative treatment of periodontal diseases (review) / O. I. Oleinik, O. P. Krasnikova, E. A. Alferova [etc.]. — Text: immediate // New tasks of modern medicine: materials of the IV International. scientific conf. (St. Petersburg, December 2016). - St. Petersburg: Own publishing house, 2016. - pp. 47-51. — URL: https://moluch.ru/conf/med/archive/239/11523/ (access date: 02/04/2022).
Modern approaches to conservative treatment of periodontal diseases (review)
Oleynik Olga Igorevna, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor;
Krasnikova Oksana Pavlovna, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor;
Alferova Elena Aleksandrovna, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor;
Kubyshkina Kristina Pavlovna, dentist-therapist;
Glazyev Viktor Konstantinovich, graduate student
Voronezh State Medical University named after N. N. Burdenko
The article is devoted to modern aspects of conservative treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases using ultrasound devices, including “Vector”, plasma lifting, antibacterial and herbal medicines, which can be recommended for various forms of pathology or accompany other types of treatment (orthopedic and surgical).
Key words: inflammatory periodontal diseases, chronic generalized periodontitis, biofilm, vector therapy, herbal remedies
Periodontal diseases are among the most common in dental practice today and affect patients of all age groups [8, p. 26].
As for the dental status of the population in the regions, an analysis of the results of the 2nd epidemiological dental survey of the population of Russia (2008) showed that in Voronezh and the Voronezh region the prevalence of signs of periodontal tissue damage among the adult population 35–44 years old is very high (more than the average for Russia is 81-87%) [9, p. 138].
A large number of scientific publications are devoted to the issues of oral microbiology, and it is considered as an extremely negative and aggressive factor that primarily determines the occurrence of pathology of the tooth and soft tissues. The issue of biofilm, which is an accumulation of microorganisms in a matrix attached to the surface of the tooth, has been studied in more depth and detail [4, p. 128].
The structural and functional state of the periodontium, like any mucous membrane, depends on the hormonal activity of the body. As practice shows, bacterial microflora is the root cause of periodontal diseases in only 20% of cases; generally, microorganisms play a secondary aggravating, but not causative, function. If they were starters, then rinses and antiseptic solutions would solve the tasks already on the 1st or 2nd day, but in practice this, unfortunately, does not happen.
The time has come to analyze the composition of the microflora of dental plaque in normal conditions, with gingivitis and periodontitis, and also to determine which microflora should be targeted for treatment procedures. The supra- and subgingival microflora differ sharply in their composition (Table 1).
Table 1
Characteristics of supra- and subgingival dental plaque
| Supragingival dental deposits | Subgingival dental deposits |
| Streptococcus sanguis | Fusobacterium nucleatum |
| Streptococcus mitis | Eikenella corrodens |
| Actinomyces naeslundii | Porphyromonas gingivalis |
| Actinomyces viscosus | Prevotella intermedia |
The main microorganism that has to be combated even during gingivitis is P.gingivalis, which has a number of pathogenic properties [3, p. 82]:
− penetrates into the epithelial cells and ligament of the tooth,
− produces leukotoxins that destroy neutrophils,
− produces enzymes that break down protein matrices,
− gram-negative bacteria produce metabolites that lyse bone.
Speaking about the disruption of microcirculation, it should be noted that during inflammation it is activated and microvessels begin to actively and continuously grow, many immature inflammatory vessels are formed, which do not have a median elastic wall, are tortuous and brittle (in the clinic they manifest themselves as bleeding gums). The afferent link of the blood flow increases, but the efferent link (venous network) does not change, which provokes venous stagnation, accumulation of metabolic toxins and extracellular fluid - tissue swelling, cellular communication and interaction are disrupted. The process enters a chronic phase and is self-sustaining, which does not allow the formation of a new periodontal ligament.
Therefore, the main way to combat inflammatory periodontal diseases (IPD) is the mechanical destruction of the supra- and subgingival biofilm, the creation of a biologically adapted tooth root surface, which helps restore the periodontal attachment; the pathogenetic link in the treatment of periodontitis is the excision of blood vessels using invasive techniques. And then, if necessary, all other methods and means (medicines) aimed at correcting inflammatory-dystrophic processes in the periodontal complex will act as effectively as possible.
At the initial stage of treatment, it is important to carry out high-quality instrumental removal of dental plaque with leveling the surface of the tooth roots. Currently, periodontology uses various methods for removing dental plaque.
Depending on the method of generating ultrasound (US), devices are divided into magnetostrictive and piezoelectric. The ellipsoidal trajectory of movement of the working tip of the magnetostrictive scaler (MS) nozzle reduces the traumatic effect of ultrasound on hard tooth tissues. The MS nozzle heats up quickly and significantly, due to this the water is heated. Careful work is ensured that does not damage the restoration structures, as well as a gentle effect upon contact with the soft tissues of the tooth, which makes the professional hygiene procedure painless and comfortable for the patient. Thus, it is now generally accepted that the use of magnetostrictive ultrasound technologies is the least traumatic method of removing dental plaque.
However, if the patient suffers from hyperesthesia, in order to completely eliminate pain during and after hardware scaling sessions, it is recommended to additionally use the therapeutic and prophylactic paste “Nupro-sensodyne” containing novamin (Ca and sodium phosphosilicate - bioactive glass), which is intended for professional cleaning and polishing teeth and combines three effects simultaneously: removing deposits, polishing, and desensitizer properties. When applied, there is an instant release of sodium ions (increase in pH), calcium and phosphorus on the tooth surface with persistent obturation of open dentinal tubules by forming a protective mineral layer.
So, the basis of the local effect on inflammatory processes in the periodontal complex is the complete elimination of mineralized and non-mineralized dental plaque, and drug treatment contributes to a more rapid disappearance of clinical signs of inflammation and an increase in the period of remission [5, p. 15].
The opinion that treatment of VZP should be comprehensive is considered well-established. In fairness, it should be noted that this is more a declaration of intent than an existing reality. The greatest practical interest among dentists is caused by drugs used for varicose veins. We are still under the impression of conservative biases, moving by inertia, ignoring both surgical and orthopedic interventions in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
Since the most serious factor in periodontal inflammation is the persistence of periodontopathogenic microflora in the oral cavity, normalization of the oral microflora is the main task of using medications of a different spectrum. Thus, the most widespread in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis (CGP) are antibacterial drugs, which in turn are divided into two main groups [6, p. 75]:
1) antiseptics - substances with low selective activity. By interacting with the proteins of microorganism cells, they cause coagulation, stopping the growth of pathogenic microflora;
2) antibiotics - substances of natural or semi-synthetic origin, which also have a direct effect against pathogenic microflora during periodontal inflammation (Mazur. R., 2000; Ovchinnikova V.V., 2002; Newman M., Van Winkelkoff A., 2004; Solovyova O. V., 2005; Salvi GE et al, 2002; Zelic O. et al, 2009).
Among the most commonly used antibiotics for inflammatory processes in the periodontium, tetracycline drugs have been widely used here and abroad (Botelho MA et al, 2007; Botelho MA et al, 2010; Botelho MA et al, 2009). Metronidazole and drugs based on it are widely used (Grudyanov A.I. et al., 2002; Kazarina JI.H. et al., 2007; Prikuls V.F. et al., 2008). Relatively recently, antibacterial drugs from the group of fourth generation fluoroquinolones began to be used in periodontology for antimicrobial chemotherapy. Moxifloxacin, gatifloxacin, gemifloxacin are significantly superior in their effect on pathogenic bacteria not only to other fluoroquinolone drugs, but also to other antibiotics that have gained recognition in dentistry (Ippolitov E. V., 2004). There is evidence of the high effectiveness of the use of antibiotics from the group of macrolides (oleandomycin, erythromycin), as well as sulfonamides. Antifungal therapy uses the polyene antibiotics levorin and nystatin. They are used in the form of 5% ointments under a bandage or in the form of solutions for applications. Antifungal drugs also include decamine and decamethoxin, the latter is used in the form of 0.01–0.02% solutions for rinsing the mouth. To combat oral Trichomonas, the antibiotic trichomonocide is used in a 1% solution [10, p. 233].
Modern trends in individualization can be seen in everything: carpules of anesthetics, capsules of filling materials, unitoses of adhesive systems, individual sachets of remineralizing gels, etc. Therefore, we periodontists must keep up with the times, making our work not only technically high-quality, but also the most individualized in the eyes of our patients.
It is necessary to create the required concentration of the drug throughout the area being treated, and further maintain the desired concentration of the drug for the required time. However, this turns out to be almost impossible due to the secretion of saliva and gingival fluid, which constantly reduce the concentration of drugs, therefore weakening or even completely stopping their therapeutic effect.
We have developed a method for long-term retention of medication on the gum mucosa by manufacturing an individual mouthguard made in the form of a monoblock on a MINISTAR thermoforming machine using thermoplastic elastic material bio- or copy plastic (Fig. 1) [2, p. 167].
Rice. 1. Type of periodontal tray
Non-drug methods that can replace or significantly limit the need for medications and at the same time affect various aspects of the pathological process are attracting more and more attention. Recently, for the treatment and prevention of periodontal diseases, the “Vector” hardware complex from Durr Dental (Germany) has been successfully used, which removes biofilm, dental plaque, tartar, endotoxins, and also quickly and effectively eliminates bacteria that cause diseases. At the same time, according to a number of authors, ozone therapy is a highly effective method of treating a number of diseases whose pathogenesis is based on inflammatory syndrome of bacterial etiology. However, during local treatment of the periodontal pocket, ozone has only a superficial antimicrobial effect. In this regard, the use of the “Vector” apparatus using ozonated water instead of distilled water is of great scientific and practical importance [11, p. 46].
When working with the “Vector” apparatus, a positive effect of hydroxyapatite suspension particles was noted, which contributed to the creation of an optimal biological state not only for the hard tissues of the tooth, but also for the regeneration of periodontal structures, and the painlessness of the procedure for the patient is of great importance in terms of the formation of his positive motivation for carrying out systematic preventive and supportive therapeutic measures [7, p. 139].
The use of the “Vector” device with ozonized distilled water during a periodontal appointment provides:
1) a persistent therapeutic effect in the majority of cases and in a shorter time (approximately 2 times) compared to traditional means;
2) when assessing the microbial status of the periodontal pocket, positive dynamics were revealed;
3) ozone therapy, unlike antibiotic therapy, has no side effects, as a result of which it can be recommended to patients with intolerance or ineffectiveness of therapy using other methods.
Plasmolifting, an injection of platelet-rich plasma obtained from the patient’s blood into the body’s tissues, is increasingly being heard today as an innovative method of treating varicose veins. The liquid fraction of blood is used. Blood is obtained from a vein, driven in a vibration-free centrifuge, along the transitional fold of the upper and lower jaw. Course of 3–5 visits with an interval of 5–6 days [8, p. 456].
In modern dentistry, treatment methods that have a pronounced positive effect with a minimum of side effects are of great interest. One such method is herbal medicine. Today, this science has become an officially recognized method of treatment and is rapidly developing. In 2016, the IV International Congress of Herbalists and Herbalists was held in Moscow on the basis of the Peoples' Friendship University of Russia, the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences and the Institute of Oriental Medicine of the RUDN University.
The most important advantages of herbal medicine over traditional methods of treatment are:
1) herbal medicines used in herbal medicine, due to the presence of various groups of biologically active substances, can have a complex effect on periodontal tissue: antiseptic, analgesic, bactericidal, bacteriostatic, anti-inflammatory, keratoplasty decongestant, etc.;
2) herbal medicines are low-toxic, their effects are mild, allergic reactions are rare, which allows, if necessary, to take them for a long time (years) without harm to the patient, since stable adaptation of the micro- and macroorganism does not develop to them;
3) herbal medicines can be recommended to patients of all age groups;
4) an important advantage of herbal preparations is also usually the pleasant organoleptic properties of biologically active substances;
5) herbal remedies also stimulate tissue regeneration processes.
In addition, medicinal plants have a positive effect on the macroorganism as a whole: they restore normal intestinal microflora, help eliminate dysbacteriosis and normalize the functioning of many internal organs, also strengthening the general immune system.
The range of plants used in modern dentistry for the treatment of CGP is quite wide. The most actively used drugs are based on oak bark, chamomile, calendula, sage, St. John's wort, yarrow, etc. One of these drugs is “Stomatofit” - a complex preparation of 7 medicinal plants. The composition of the drug includes: calamus root, oak bark, sage leaves, arnica herb, peppermint leaves, chamomile flowers, thyme herb. "Stomatofit" helps relieve inflammation, irritation, pain, burning, swelling, reduce bleeding gums and bad breath.
A special place among the drugs used in herbal medicine is occupied by the systemic drug “Ginkoum”. It is created on the basis of the relict plant Ginkgo biloba. Interest in ginkgo arose in the 50s of the 20th century. in Western Europe, when its clinical and laboratory studies began. During that period, for the first time, scientists established the angioprotective and antioxidant properties of ginkgo leaves. Currently, in America, various preparations based on ginkgo biloba are among the top five most purchased medicines. In France, ginkgo biloba leaf extract is one of the most commonly prescribed drugs, and in Germany it is recognized as the most popular. Ginkgo leaf extract has a complex chemical composition; it contains more than 40 biologically active ingredients, which together cause a huge number of positive effects. Ginkgo biloba stimulates the biosynthesis of substances that dilate blood vessels in the brain, increases blood flow in the arterial, venous and capillary beds, which increases the consumption of oxygen and glucose by tissues and cells. This effect also helps prevent high blood pressure and helps avoid complications such as blood stagnation in peripheral vessels. Regular use of drugs based on it helps restore blood flow in areas with vasomotor paralysis. Ginkgo biloba also reduces the concentration of cholesterol in the blood. It has an antioxidant effect, which is expressed not only in the destruction of existing free radicals, but also in the inhibition of the formation of peroxide compounds from membrane lipids (Kalikinskaya E., 2000). The vasodilating effect noted in studies, an increase in blood flow in the capillary bed in peripheral vessels, as well as antihypoxic and anti-edematous effects distinguish this drug from others.
Since any pathological process in the oral cavity is associated not only with an inflammatory reaction, which is caused by microbial aggression, but also with microcirculatory disorders, the main role in the development of which is played by impaired blood flow in the capillaries, the use of this drug opens up new horizons in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
Thus, herbal medicine is one of the promising areas in modern dentistry, since herbal medicines have a mild complex effect on the body as a whole, are non-toxic, non-allergic, and can be used in all age groups. They are effective in prevention and long-term treatment, and are also a worthy alternative to antibacterial drugs.
In the algorithm of conservative treatment of mild chronic generalized periodontitis, along with antiseptic drugs, it is necessary to include drugs that stimulate blood flow in the periodontium, since the restoration of microcirculation in the affected tissues under the influence of antibacterial drugs does not occur completely. According to the studies, the best results were shown by the complex of herbal remedies “Forest Balsam” and “Ginkoum”. After professional oral hygiene, it is recommended to prescribe herbal preparations according to the following scheme: “Forest balm” 2–3 times a day for 14 days, “Ginkoum” 1–2 capsules 3 times a day for at least 8 weeks [1, p. 622].
Thus, periodontium is a multifaceted and very interesting area of our body; it requires deep study and scrupulous attitude towards oneself. The timing of the onset of clinical well-being and the duration of the period of remission are individual and depend on many factors: age, the presence of general somatic pathology, the severity of the disease, unfavorable local factors, the biotype of the gums, which should be taken into account by the dentist in clinical practice.
Literature:
- Antonova M.V., Sushchenko A.V., Svirina M.S. An integrated approach to the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis using herbal medicine // System analysis and management in biomedical systems. – 2012. – T. 11, No. 3. – P. 622–625.
- Burdina G. A. Application of a modified soft orthodontic mouthguard in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases / G. A. Burdina, O. I. Oleinik // Bulletin of new medical technologies. - 2010. - T. ХVII, No. 2. - P. 167–169.
- Vysochanskaya Yu. Innovations in the field of periodontology / Yu. Vysochanskaya // DentArt. – 2104. – No. 1(74). – P. 80–86.
- Microbiology and immunology for dentists: transl. from English / ed. R. J. Lamont [et al.]. - Moscow: Practical Medicine, 2010. - 504 p.
- Oleinik O.I. Development of methods and evaluation of the effectiveness of the results of individual prevention and inflammatory periodontal diseases: abstract. dis. doc. honey. Sci. – Voronezh, 2014. – 46 p.
- Oleinik O.I., Vusataya E.V., Popova V.S. An integrated approach to the treatment of early forms of inflammatory periodontal diseases // Young scientist. – 2015. – No. 5(85). – pp. 75–78.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of using a vector system in the complex treatment of patients with moderate chronic generalized periodontitis / O. I. Oleinik, M. A. Sorokina, S. V. Erina, K. P. Kubyshkina // Bulletin of new medical technologies. - 2013. - T. XX, No. 2. - P. 138–143.
- Periodontology: national guide / ed. L. A. Dmitrieva. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2013. - 712 p.
- Dental morbidity in the Russian population. Condition of periodontal tissues and oral mucosa / ed. O. O. Yanushevich. - Moscow: MGMSU, 2008. - 228 p.
- Fedi P. Periodontal ABC / P. Fedi, A. Vernino, D. Gray. — Moscow: Publishing house. House "Azbuka", 2005. - 287 p.
- Khotit R. A. The use of the VECTOR device in the complex therapy of periodontal diseases / R. A. Khotit // Dental South. - 2006. - No. 3. - P. 46–47.
Key terms
(automatically generated)
: drug, inflammatory periodontal disease, treatment of periodontal diseases, modern dentistry, dental plaque, capillary bed, required drug concentration, pathogenic microflora, pathological process, plant origin.
What happens if periodontal inflammation is not treated?
Often patients, if gum inflammation is not accompanied by pain, treat it rather frivolously, letting the situation take its course. This is a fundamentally wrong and even dangerous position. Periodontal diseases can be successfully treated in the initial stages. In advanced cases, enormous efforts by doctors will be required to save the patient’s teeth from falling out. And the patient’s quality of life will deteriorate significantly. He will be haunted by constant pain and bad breath. He will not be able to eat normally, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract will appear or worsen. The infection can penetrate through the bloodstream into any of the organs and cause complex diseases, including the development of sepsis.
Remember: the lack of treatment for periodontal inflammatory processes can result in tooth loss and death caused by sepsis. Do not delay visiting a doctor when the first symptoms of gum inflammation appear. Take care of your health!
How Vector works
It is the use of the Vector device that is the gold standard of modern periodontology. It generates ultrasonic vibrations of a strictly defined frequency, under the influence of which tartar is separated from the surface of the enamel. The doctor runs a thin tip over the surface of the teeth, paying special attention to the cervical area. A water jet irrigating the tip of the device washes away deposits from under the gums. The procedure has a polishing effect. The surface of the teeth becomes smoother, which means plaque formation slows down. Treatment of gums in periodontology in Moscow today is impossible to imagine without Vector-therapy. Its effectiveness and safety are time-tested. Patients note positive dynamics after the first procedure: swelling, pain, and itching decrease. The gum tissue becomes evenly colored and denser. If you have any questions regarding treatment with the Vector device, you can contact our doctor during your initial consultation.
Advantages of Vector therapy
- The procedure does not harm tooth enamel;
- Allows you to completely remove microbial film from the tooth surface;
- Positive effect already 2-3 days after the procedure;
- Periodontal pockets are cleaned without curettage, without surgical intervention;
- No anesthesia is required and the procedure is well tolerated.
The procedure has a powerful healing effect. It has proven itself well and is used all over the world. The peculiarity of conservative periodontology is the repeated nature of the impact. If surgical intervention is performed once, then conservative methods usually require a course of use. Cleaning with the Vector device is usually carried out twice with an interval of 1 month.
Conservative treatment of periodontitis
Periodontitis today, along with caries, is one of the most common diseases of the oral cavity. It is an inflammatory process localized in the area of one or more teeth. The course of periodontitis is accompanied by the formation of periodontal pockets. Bacteria and food particles accumulate in them, which leads to swelling, soreness, suppuration and bad breath. Treatment tactics are selected individually, taking into account the root cause of the disease.
General treatment regimen
As a rule, conservative therapy includes the following steps:
Stage 1
– elimination of common factors that provoke gum disease:
- Training in oral hygiene rules. Maintaining hygiene during treatment and subsequent remission is of paramount importance.
- Professional oral hygiene. Cleaning helps remove plaque and hard deposits. This contributes to the creation of an apathogenic environment in the oral cavity.
- Treatment of caries. It must be carried out without fail to eliminate foci of proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
During the examination, the doctor can identify what was the root cause of the development of periodontal disease. In some cases, this may be an incorrect bite or poorly selected orthopedic structures. In this regard, the patient is referred for consultation to a specialized specialist: an orthodontist or an orthopedist. Elimination of the factor that became the trigger leads to a significant improvement in the condition of the oral cavity.
Stage 2 – elimination of the inflammatory process in the gum tissue
After professional oral hygiene or Vector therapy, the gums are treated with antiseptic agents. The doctor also prescribes ointments, elixirs, oral baths, mouth rinses, antiseptics, etc. for home use. The choice of medications is carried out according to indications on an individual basis.
Stage 3 – elimination of periodontal pockets
If conservative methods fail to stop the inflammatory process, curettage of periodontal pockets is performed. The procedure can be performed open or closed. The doctor completely cleans the pocket of pathogenic microorganisms, dead epithelial cells, food particles, and deposits. The surface of the root is polished, the pocket is washed with antiseptic compounds. Don't be afraid of curettage. The intervention is performed locally using anesthesia. The tissues of the gums and oral mucosa regenerate very quickly, so the healing process does not take much time. The doctor will set a date for a follow-up examination to evaluate the results of the curettage and decide on a further plan of action.
Stage 4 – recovery period
During the recovery period, it is very important to follow the recommendations of your doctor. First of all, this concerns the rules of oral hygiene. Also, you should avoid injuring the problem area. Do not eat too hot, spicy, or hard foods until the gum tissue has completely healed.
Stage 5 - clinical monitoring of the patient’s condition
Each patient who has been diagnosed with periodontitis must visit a doctor 2 times a year for monitoring and routine professional oral hygiene. Other problems that arise should be resolved in a timely manner: treat caries, carry out dental prosthetics if necessary. This set of measures will allow you to maintain the oral cavity in order and avoid relapse of the disease and associated inconveniences.
Splinting teeth
Another equally dangerous disease is periodontal disease. It is less common and is not inflammatory, but atrophic in nature. The bone tissue of the alveolar process of the jaw changes its structure, becomes looser, gradually collapses, and the height of the partitions between the teeth decreases. As a result, the teeth become mobile and fan out. To prevent their further loosening and create conditions for the restoration of the tissues surrounding the tooth, splinting is performed. To do this, use thin white fiberglass tape. On the unnoticeable surfaces of the teeth (lingual, chewing), a groove is formed into which the tape is placed. It allows you to reduce the range of tooth movements.
Recommendations from prevention experts
- Regular and thorough oral hygiene twice a day
- Cleaning teeth after every meal (rinsing, flossing)
- Course use of special preventive toothpastes
- Complete balanced nutrition
- Compliance with all medical prescriptions for the treatment of diabetes and other serious diseases
- Maintaining immune status at the proper level
- Quitting smoking (reducing the number of cigarettes you smoke)
The network of dental clinics “Smile” offers periodontology services: treatment of gum inflammation. Contacting our centers has several significant advantages:
- We employ highly qualified specialists;
- we follow diagnostic and treatment protocols that meet international standards;
- We use a system of family and cumulative discounts;
- we guarantee a stable cost of treatment according to the approved price list.
You can contact any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Do not delay your visit to the periodontist; make an appointment as soon as the first symptoms appear. This will significantly shorten the duration of therapy and reduce costs. Our doctors will provide effective dental care regardless of the severity of the disease. We will take care of your health!