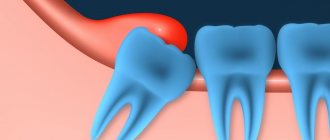
Fused teeth are one of the rarest anomalies in the development of the dental-jaw system, which consists in connecting the sides of the rudiments during the development of the embryo. It occurs in only 1% of Patients.
Most often, fused teeth are observed during a primary dentition; with a permanent dentition, such an anomaly is extremely rare.
The reasons for the formation of fused teeth can be:
- hereditary factor;
- too much pressure on the buds of neighboring teeth;
- jaw injuries;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases that cause metabolic disorders in the human body.
Often, the fusion of teeth is confused with their fusion, although these pathologies are completely different in nature. Teeth fusion occurs during the period after their growth and development, and fusion occurs during the formation of tooth buds.
What is ankylosis
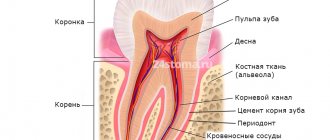
Tooth ankylosis is a pathology characterized by fusion of the cement of the tooth with the jaw bone. The tooth root is deprived of part of the ligamentous apparatus, which often leads to adhesion or germination of bone tissue. The aesthetics of the teeth are disrupted, they look shorter and change their angle. Ankylosis usually occurs during tooth eruption. Pathology can also form at a late stage in the formation of the dental arch.
It is important to know. The process is accompanied by periodontal necrosis and the incorporation of root cement into the alveolar bone.
Ankylosis of a primary tooth is caused by loss of the periodontal ligament. It is observed in cases where a primary molar does not fall out due to the absence of a permanent dental unit. Ankylosed teeth are different in size from their neighbors, so bite correction will be required.
Types of Teeth Fusion
In orthodontics, there are several types of dental fusion:
- first: supernumerary fusion. In this case, the second tooth is much smaller than the first. It is characterized by a spiky shape and a bumpy surface;
- second: non-gingival, observed only in the supragingival part involving a certain area of enamel;
- third type: root. Occurs in the root part at the level of cement and is characterized by deep damage to dentin. At the same time, both teeth have the same size;
- fourth: observed along the entire height of the tooth with damage to the crown and root parts.
Symptoms
Parents should be wary of the fact that their child’s baby teeth are not falling out. It is fused to the bone and cannot easily separate from the alveoli, as is normal. If the pathology is not detected and treated in a timely manner, the child’s jaw begins to develop incorrectly. The diseased tooth is located lower than the others, and the neighboring teeth are placed at an angle in relation to it. Problems with bite occur.
Another scenario is also possible. The baby tooth does not erupt completely and is delayed in its development. Because of this, the permanent tooth also cannot develop, and after the milk tooth falls out, it becomes fused with the jaw. This is how ankylosis of permanent teeth occurs. The final diagnosis is made after analyzing the results of a computed tomography scan.
Good to know. The service life of ankylosed teeth is completely different. They can last for decades or fall out, thinning out the dentition.
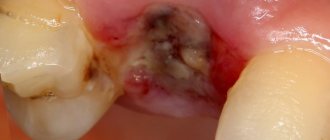
Impacted supernumerary teeth
Often, supernumerary teeth stop growing and remain impacted, that is, unerupted. Such teeth may not appear for a long time; they are discovered by chance during an X-ray examination of the oral cavity. The presence of an impacted supernumerary tooth may be indicated by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of mobility of complete teeth;
- periodic aching pain in the area where the tooth is located;
- tissue compaction if the tooth is located close to the edge of the jaw.
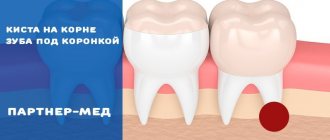
Cysts sometimes develop on the root of the tooth, which may not cause pain for some time; they are also detected during x-ray examination.
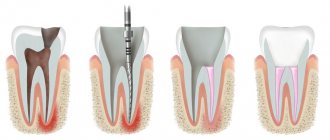
Treatment of ankylosis
Treatment of ankylosis with traditional orthodontic methods (braces) is impossible. The tooth grows into the bone and it is impossible to return it to its correct position. But restoring the functionality of the dentition is quite possible. In dental clinics, the method of treatment is selected individually in each individual case.
First of all, the patient is referred for a dental computed tomography scan. The dental surgeon studies panoramic images and draws up a treatment plan. Most often, surgical treatment methods are used: excess fibrous tissue is removed and joint mobility is restored. Crowns made of metal-ceramics, ceramics and zirconium dioxide are also used to treat dental ankylosis. With their help, the bite is corrected.
Correction methods
Several years ago, the only method of correcting fused teeth was to remove them. Modern orthodontics offers more advanced ways to eliminate this anomaly, allowing you to leave the tooth intact.
As a rule, treatment depends on the type of pathology:
- in the first type, correction is carried out by careful grinding of the adjacent part of the tooth and subsequent restoration;
- in the second type, hemiresection is performed - that is, detachment and removal of the adjacent part without traumatic effects on the periodontium;
- the third type requires hemisection - detachment of the gum tissue and incision of the root part;
- with the quarter type, hemisection is carried out along the entire length of the teeth.
Stages of treatment
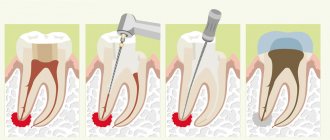
Correction of teeth fusion is carried out in several stages:
- The first stage is the removal of the secondary part of the tooth. When cutting off the upper part, conduction anesthesia is used, and in case of complete dissection, general anesthesia is used. Hemiresection is carried out using a diamond disc, and a two-week bandage is applied to the wound. Hemisection is a more traumatic procedure performed with a scalpel. Sutures are placed on the dissected mucosal flaps, which are removed after a week, and the tooth is splinted for two weeks;
- the second stage - orthodontic, begins two weeks after the separation of the teeth. Its goal is to restore normal occlusion. Most often it is corrected with a braces system.
Modern orthodontics makes it possible to treat fused teeth, restoring their normal appearance and preserving the pulp in 90% of cases.
Prognosis and prevention
Consilium Dent clinic uses advanced methods of therapeutic, surgical, and orthopedic treatment of dental anomalies in patients. By skillfully combining them, experienced specialists are able to restore the aesthetics of a smile and ensure the normal functioning of the dental system, even if the degree of deviation is significant.
Prevention of anomalies in the formation and development of dental units begins during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus and is carried out throughout a person’s life. The main stages are as follows: monitoring the successful course of the prenatal period, caring for harmonious postnatal development, organizing a correct lifestyle while the baby is growing up, caring for dental health and general health throughout life. By conducting an annual preventive examination, the dentist identifies dental anomalies at an early stage, when the pathological process is still reversible.
Expert of the article you are reading:
Classification of missing teeth according to the location of the disease
| By localization | Description |
| Missing upper teeth | The absence of teeth in the upper jaw can be either partial or complete, as well as single. |
| Missing lower teeth | A general designation for a disease indicating the absence of teeth in the lower jaw. |
| Lack of chewing teeth | May be referred to as missing lateral teeth. Lack or complete edentulism in the chewing region. In particular, we are talking about the absence of small molars (premolars) and molars. |
| Missing front teeth | Edentia of incisors or canines in the frontal zone. |
In addition to the classification described above, the type of teeth itself is also taken into account. Based on this, the absence of molars and edentulous primary teeth (not associated with the normal timing of their replacement) are distinguished.
Deformations of the dentition
The pressure exerted by the erupting wisdom tooth on the dentition when there is not enough space causes crowding of the teeth in the dentition and the development of malocclusion. Aesthetics and smiles are affected mainly in the anterior region, and oral hygiene becomes difficult.
Growing and expanding wisdom teeth are often the cause of reoccurrence of malocclusion after long-term orthodontic treatment. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to remove wisdom teeth before starting orthodontic treatment!
Indications for wisdom teeth removal can be formulated as follows: ANY DISEASE, COMPLICATION ASSOCIATED WITH WISDOM TEETH, AS WELL AS THE RISK OF THESE DISEASES OR COMPLICATIONS IS A DIRECT INDICATION FOR WISDOM TEETH REMOVAL.
Classification of edentulism by the number of missing teeth
| Number of missing teeth | Classes | general description |
| Partial edentia (ICD K00.00) | Partial primary adentia. Partial secondary adentia. | With partial edentia, from one to 5 teeth or their rudiments are missing on one jaw. Most often, three teeth are missing. |
| Multiple edentia | Multiple primary adentia. Multiple secondary adentia. | Many experts combine the concepts of partial and multiple edentulism. Criteria:
And so on up to 15 units on one jaw. |
| Complete edentia (ICD K00.01) | Complete primary adentia. Complete secondary edentia. | Complete absence of teeth or missing teeth |
Primary and secondary edentulous teeth
Experts distinguish several types and subtypes of adentia. For greater convenience, below are tables showing the types of the disease, combined by certain characteristics.
Primary adentia
Caused by hereditary factors and diseases at the stage of fetal formation. With primary adentia, there is an absence of tooth germs.
Varies:
- partial primary adentia - the absence of one or more rudiments (for example, primary adentia of two incisors);
- complete primary adentia – absence of all tooth buds. It is extremely rare;
- true adentia – absence of tooth buds (without their destruction by diseases and infections);
- false edentia, when different teeth merge into one.
Secondary adentia
Secondary adentia occurs as a result of illness and injury during life.
Reasons causing anomalies
Anomalies of the dental system are very diverse and include both anomalies of dental units and incorrect formation of the dentition, as well as abnormalities in the development of the jaws. The most frequently diagnosed abnormalities of dental units. They can be caused by a wide variety of reasons, including both exogenous (caused by external factors) and endogenous (formed as a result of the physiological state of the patient).
Endogenous causes
Endogenous anomalies are formed as a result of genetic and endocrine disorders.
- Many structural features of the dental system, leading to improper development of teeth, are genetically determined. This can occur through direct inheritance (abnormal number and shape of teeth, edentia, diastema), through inheritance of a mismatch in the size of the jaw bones, through inheritance of a mismatch in the size of the jaw and teeth (crowding of teeth or sparse arrangement of teeth). Dental anomalies of this type include disorders associated with hereditary and congenital pathologies (clefts of the soft and hard palate, cleft lip, Down syndrome, Vaanderburg syndrome, Seckel syndrome, Shershevsky-Turner syndrome).
- Another part of the endogenous causes of dental anomalies are problems of the endocrine system, such as hypothyroidism (in later stages), hyperparathyroidism, hypocortisolism. Their frequent symptoms may be delays in the eruption and replacement of teeth, and disturbances in the formation of the enamel layer.
Exogenous causes
Exogenous (external) causes of dental anomalies are, for the most part, external unfavorable factors that affect the baby’s body during the formation of tooth germs. There are prenatal (prenatal), postnatal (postpartum) and intranatal (associated with childbirth) periods.
- An example of a prenatal factor is a pregnant woman living in poor environmental conditions. Various developmental disorders of the fetus can also occur as a result of the mother’s poor lifestyle.
- Factors in the intranatal period may include complicated labor, birth injuries, consequences of asphyxia and oligohydramnios.
- In the postnatal period, dental anomalies develop as a complication of pathologies in early childhood. These include childhood infections, rickets, hypovitaminosis, and micronutrient deficiency.
All these reasons are of a common nature. Local factors that affect dental development include everything related to improper oral care, feeding errors or bad habits. Among them are feeding too soft food, prolonged sucking of a pacifier or finger in early childhood.
Childhood injuries and caries with complications lead to dental anomalies.
The death of tooth germs or the development of supernumerary teeth can occur due to osteomyelitis.